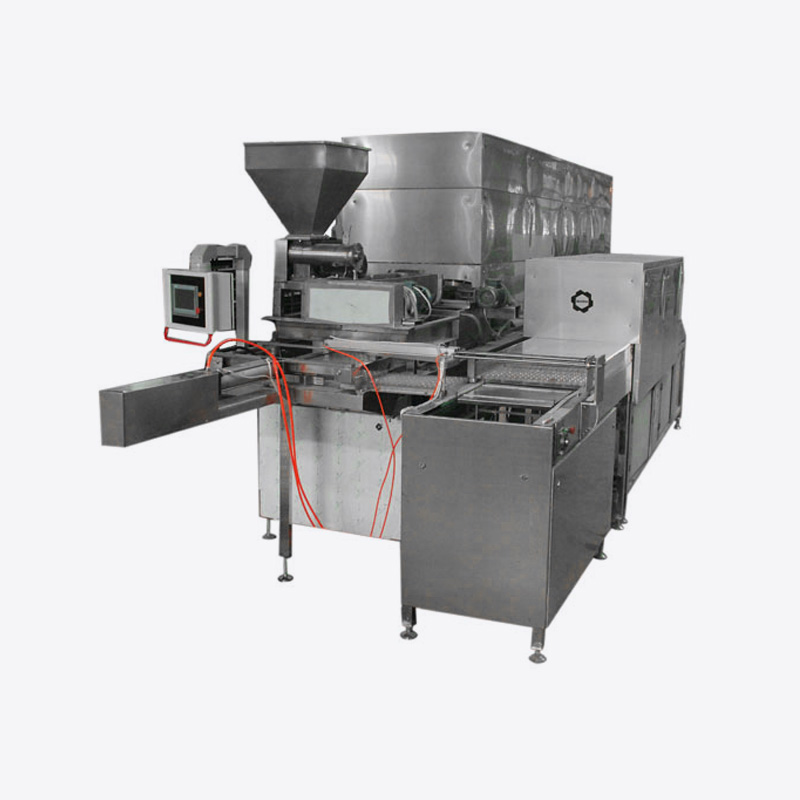
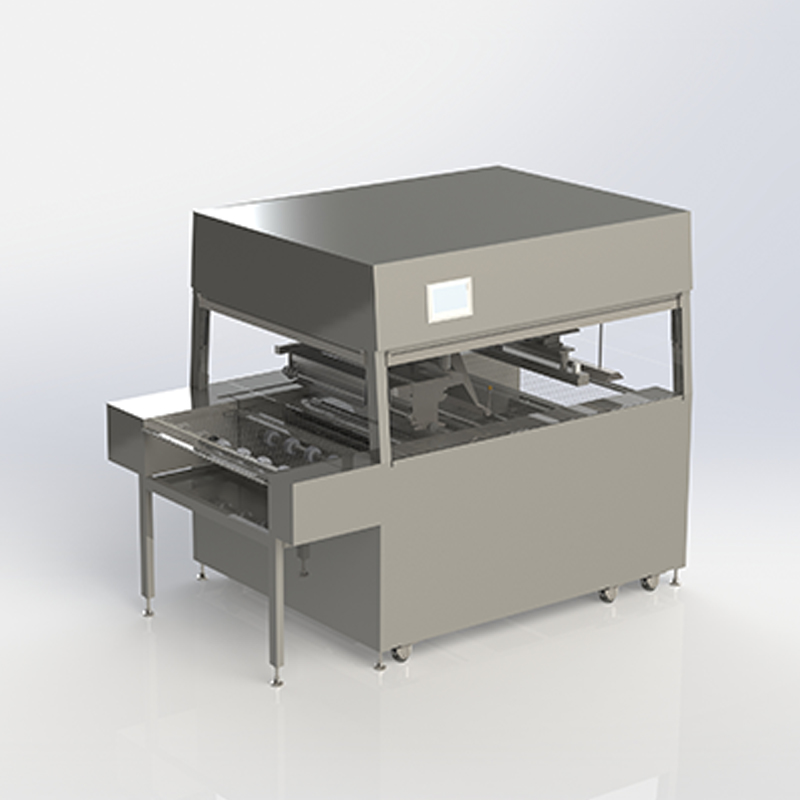
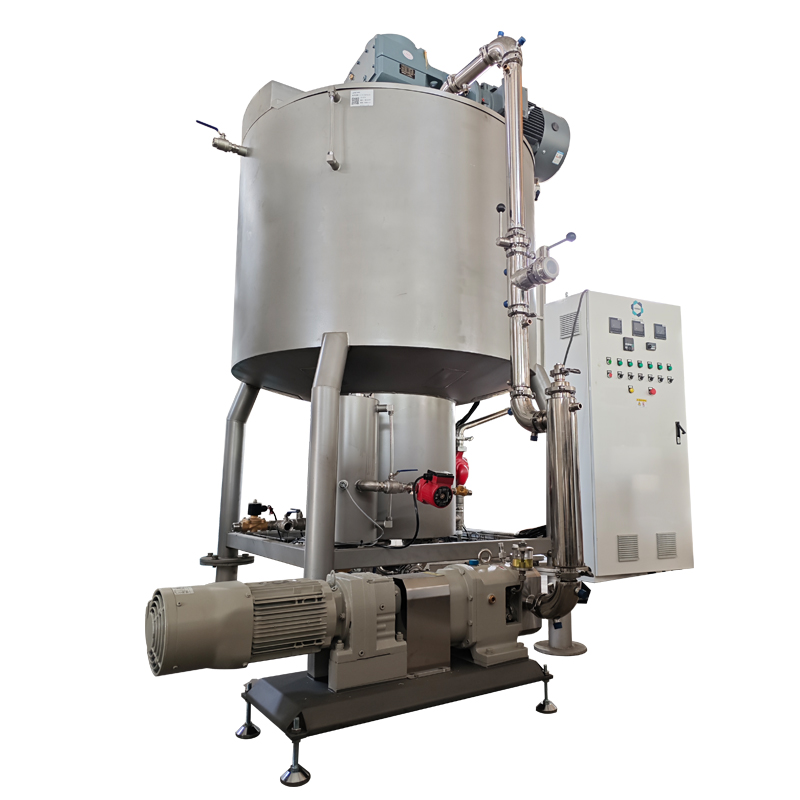
What is a Food Machine?
A food machine is a device or piece of equipment specifically designed to automate, assist, or enhance the process of food preparation, processing, packaging, or preservation. These machines are critical in both commercial and industrial food production, helping businesses scale up operations, improve efficiency, and maintain product consistency. The range of food machines is vast, encompassing everything from simple kitchen gadgets to large industrial machinery used in factories.
Food machines are used in various stages of food production, including processing raw materials, mixing ingredients, cooking, freezing, packaging, and storing food products. These machines are essential for ensuring the efficiency, hygiene, and safety of food production, making them indispensable in both small kitchens and large-scale manufacturing plants.
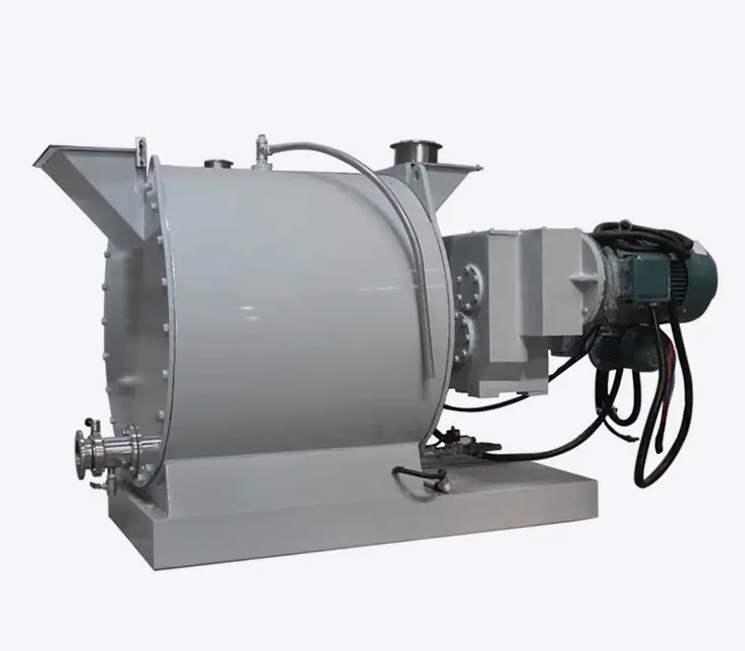

What Are the Different Types of Food Machines?
Food machines are essential tools in the food production industry, designed to automate, streamline, and improve various stages of food processing, packaging, and preservation. These machines have revolutionized the food industry, enabling manufacturers to meet growing demands, ensure consistency, and improve overall efficiency. Depending on the specific tasks they perform, food machines can be classified into several categories, each serving a unique purpose.
Here's an overview of the different types of food machines commonly used across various industries:
1. Food Processing Machines
Food processing machines are used to prepare raw ingredients for further processing or cooking. These machines can cut, grind, mix, knead, chop, and blend ingredients into a form suitable for cooking or packaging.
Examples:
Blenders & Mixers: Used for blending ingredients or mixing dough.
Grinders & Choppers: Used to break down large pieces of food into smaller sizes or desired forms, such as grinding meat or chopping vegetables.
Slicers: These are used to slice food items like cheese, vegetables, and meats into consistent sizes.
Kneaders: Specifically designed for dough preparation in baking industries.
2. Cooking and Baking Machines
Cooking and baking machines are designed to apply heat to food products for preparation. These machines are used in kitchens, bakeries, and large-scale food production to cook, bake, fry, or steam various food items.
Examples:
Ovens & Convection Ovens: Used for baking bread, cakes, cookies, and other pastries.
Fryers: Used for frying foods like fries, chicken, or doughnuts.
Grills and Roasters: These machines are used to roast meats or vegetables, often in commercial kitchens.
Steamers: Used to steam food, such as vegetables or seafood, to retain their nutrients and flavors.
3. Packaging Machines
Packaging machines are crucial for sealing, labeling, and protecting food products after they’ve been processed. These machines ensure the food remains fresh, secure, and tamper-proof during transportation and storage.
Examples:
Filling Machines: These machines fill containers (like bottles or jars) with liquids, semi-liquids, or solid food items.
Capping Machines: Used to securely seal bottles or containers with caps to ensure product safety and freshness.
Sealing Machines: These machines are used to seal bags, pouches, or other packaging materials to preserve food products.
Labeling Machines: These are used to apply labels to food packaging, ensuring that nutritional information and branding are clearly visible.
4. Freezing and Refrigeration Machines
These machines are designed to preserve perishable foods by lowering their temperature, which helps prevent spoilage and extends the product's shelf life. Freezing and refrigeration machines are vital for both storage and transport of items like fruits, vegetables, meats, and dairy products.
Examples:
Blast Freezers: Used to rapidly freeze food products, maintaining their quality and texture.
Cold Storage Units: These large-scale refrigeration systems are used to store perishable food products for extended periods.
Chillers: Used to keep food items at lower temperatures to preserve freshness, such as in dairy processing or seafood handling.
5. Cleaning and Sorting Machines
Food processing often involves cleaning raw ingredients to remove dirt, pesticides, or contaminants. Sorting machines are also used to separate food items based on size, shape, or quality.
Examples:
Washing Machines: Used for cleaning fruits, vegetables, and other food products before processing.
Sorting Machines: These machines sort food products based on weight, size, or color, ensuring uniformity and quality control.
Peeling Machines: These machines remove the skin or outer layer of fruits, vegetables, or other food items.
6. Food Inspection and Quality Control Machines
Food safety and quality are paramount in the food industry. Inspection and quality control machines are used to ensure that the final product meets health, safety, and regulatory standards.
Examples:
Metal Detectors: These machines are used to detect metal contaminants in food products during production.
X-ray Machines: Used for detailed inspection, detecting any foreign objects that may be present in packaged food.
Weight Checkers: Ensure that the products are of the correct weight and that packaging is consistent.
Differences Between the Types of Food Machines
The various types of food machines serve distinct purposes in the food production process. While some machines are designed for processing raw materials, others handle cooking, packaging, storage, or inspection. Here's a comparative summary in the table below:
| Type of Food Machine | Purpose | Key Functions | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing Machines | Prepare and process raw ingredients before cooking or packaging. | Grinding, chopping, mixing, kneading, and blending. | Grinders, Blenders, Mixers, Slicers |
| Cooking and Baking Machines | Apply heat for cooking or baking food products. | Baking, frying, roasting, and steaming. | Ovens, Fryers, Grills, Steamers |
| Packaging Machines | Package food products to maintain freshness and safety. | Filling, capping, sealing, and labeling. | Filling Machines, Sealing Machines, Labelers |
| Freezing and Refrigeration Machines | Preserve perishable foods by lowering their temperature. | Freezing, chilling, and storing food. | Blast Freezers, Chillers, Cold Storage Units |
| Cleaning and Sorting Machines | Clean raw ingredients and sort them based on quality or size. | Washing, sorting, peeling, and separating. | Washing Machines, Sorting Machines, Peelers |
| Inspection and Quality Control Machines | Ensure food products meet safety and quality standards. | Detection of contaminants, weight checks, and visual inspections. | Metal Detectors, X-ray Machines, Weight Checkers |
Why Are Food Machines Important?
Food machines play a crucial role in improving the quality, efficiency, and safety of food production. Here are some key reasons why they are indispensable:
Efficiency and Speed:
Machines are designed to operate much faster than manual processes. This increased speed allows businesses to meet high-demand production requirements, reducing the time it takes to process large quantities of food.
Consistency and Precision:
One of the challenges in food production is ensuring consistency across batches. Food machines, due to their precision and automation, ensure that each batch of food meets the same quality standards, whether it's the size of a cookie, the texture of a dough, or the weight of a packaged item.
Food Safety:
Food machines help maintain hygiene and food safety standards by reducing human contact and minimizing the risk of contamination. Many machines are equipped with safety mechanisms to ensure food is processed under controlled and sanitary conditions.
Cost Reduction:
Though the initial investment in food machines can be high, they ultimately help businesses save money by reducing labor costs, minimizing waste, and optimizing the use of raw materials. Over time, these machines increase the profitability of food production operations.
Scaling Production:
As demand for food products increases, it becomes necessary to scale up production. Food machines allow businesses to increase their output without compromising quality. This scalability is critical for companies looking to expand their market presence.
Innovation and Customization:
Modern food machines are increasingly customizable to meet specific production needs. For instance, machines can be adjusted to handle different types of ingredients, produce unique shapes, or meet specific dietary requirements. Innovations in food technology are also leading to new machine designs that improve the way food is prepared, packaged, and distributed.
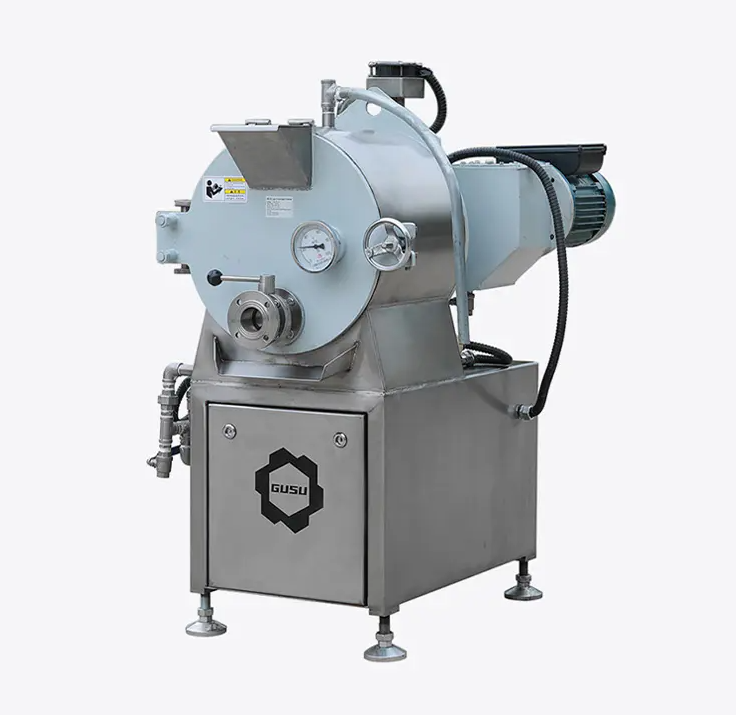

How Do Food Machines Improve Efficiency in Food Processing?
Food processing is a critical aspect of the food production industry, as it directly influences product quality, safety, and overall production output. Food machines are designed to automate and optimize various stages of food processing, from handling raw ingredients to final packaging. By integrating advanced technology, these machines significantly improve efficiency, helping businesses meet increasing demand, reduce production costs, and ensure consistent product quality. Below, we explore how food machines enhance efficiency in food processing across different stages.
1. Automation of Repetitive Tasks
One of the primary ways food machines improve efficiency is by automating repetitive tasks that would otherwise require significant human labor. Processes such as mixing, chopping, grinding, and packaging can be automated, allowing machines to operate continuously without the need for breaks or supervision. This results in:
Faster Processing: Machines can complete tasks more quickly than humans, which is particularly beneficial when processing large volumes of food.
Consistent Output: Automation ensures that the process is performed the same way every time, reducing errors and ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications.
2. Increased Production Speed
Food machines are built for speed. Their ability to work rapidly and continuously allows manufacturers to meet high production demands without sacrificing quality. For example:
High Throughput: Machines such as high-speed mixers, grinders, and slicers can process large quantities of raw materials in a short amount of time, increasing the overall throughput of the production line.
Faster Cooking and Baking: Automated cooking and baking machines, such as ovens, fryers, and steamers, can process food products faster than manual methods, cutting down production time and improving overall plant efficiency.
3. Minimized Human Error
Human error is a natural part of manual food processing, and it can lead to inconsistencies, safety issues, or even costly product recalls. Food machines are engineered to work with high precision, minimizing errors caused by fatigue, misjudgment, or manual inconsistencies. Some benefits include:
Uniformity in Processing: Machines ensure that every batch is processed the same way, whether it's slicing vegetables, mixing ingredients, or frying food.
Precision and Accuracy: Modern food machines are equipped with sensors and control systems that allow for precise measurements, ensuring that ingredients are mixed in the right proportions or that food is cooked to the exact temperature.
4. Reduction of Labor Costs
By automating key tasks, food machines help reduce the need for manual labor. This leads to a reduction in labor costs and the need for human resources, allowing businesses to allocate their workforce to other areas, such as quality control or management. Additionally:
Lower Operational Costs: As machines can operate continuously without breaks, businesses can run 24/7 without having to hire additional staff for overtime or night shifts.
Reduced Training Time: Since food machines are designed to be user-friendly, the time and costs associated with training workers are reduced.
5. Improved Product Consistency and Quality
Food machines help ensure that the final product meets the desired quality standards, contributing to improved consistency. Automated systems are designed to maintain uniformity throughout the entire production process. Benefits include:
Standardization of Products: Machines ensure that food products are of uniform size, texture, and appearance. Whether it’s dough, snacks, or packaged meals, machines help maintain the consistency needed to meet consumer expectations.
Minimized Waste: Food machines are equipped with precise control systems that minimize waste during production. For example, cutting and packaging machines ensure minimal scrap material, leading to better material utilization.
6. Optimization of Resource Usage
Efficiency in food processing is not limited to production speed or labor cost reduction—resource optimization is also a key factor. Food machines help maximize the use of raw materials and energy, leading to more sustainable and cost-effective operations:
Material Efficiency: Machines such as slicers and grinders ensure that ingredients are processed in the most efficient manner, with minimal waste. For instance, meat grinders are designed to use every part of the raw material, minimizing offcuts.
Energy Efficiency: Many modern food machines are designed to be energy-efficient, using less electricity and producing less heat, which helps reduce energy costs and minimizes environmental impact.
7. Enhanced Food Safety and Hygiene
In food processing, maintaining high hygiene standards is critical to ensuring the safety of the product. Food machines help reduce human contact with food, lowering the risk of contamination. Key points include:
Sanitation Standards: Automated cleaning cycles and sterilization features in food machines, such as in packaging or processing equipment, ensure that machines remain hygienic and compliant with food safety regulations.
Reduced Handling: By automating processes like filling, capping, and sealing, food machines limit the amount of human contact with food products, which reduces the risk of contamination from external sources.
8. Data-Driven Insights for Process Optimization
Many modern food machines are equipped with advanced data analytics capabilities that allow businesses to monitor, analyze, and optimize their production processes. With the ability to gather real-time data on machine performance, temperature, humidity, and speed, businesses can:
Optimize Production Schedules: By analyzing machine performance, businesses can adjust production schedules, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance: With real-time data, food machines can be monitored for signs of wear or malfunction, allowing manufacturers to perform maintenance proactively and avoid unexpected downtimes.
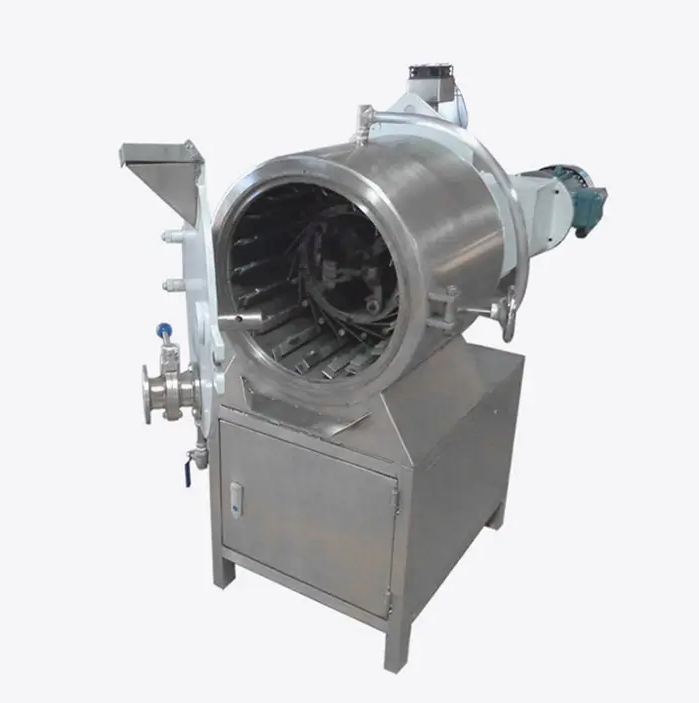

How Do You Choose the Right Food Machine?
Choosing the right food machine for your business is a critical decision that can significantly impact the efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness of your food production process. With the wide variety of food machines available on the market, selecting the right one can seem overwhelming. However, by carefully considering several key factors, businesses can make an informed decision that aligns with their production needs and goals.
Here are the key steps and considerations to help you choose the right food machine:
1. Understand Your Production Needs
The first step in choosing the right food machine is understanding your specific production requirements. Ask yourself the following questions:
What type of food product are you producing?
Different types of food products require different types of machines. For example, a bakery will need ovens, mixers, and dough kneaders, while a beverage production line will need filling and capping machines.
What volume of production do you need to achieve?
The scale of your production determines the size and capabilities of the machine you will need. A small-scale artisanal operation may need a compact, manual machine, while a large industrial plant may require high-capacity, fully automated systems capable of handling massive volumes.
What is the required level of automation?
Consider whether you need manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated machinery. Fully automated systems can reduce labor costs and improve efficiency but come at a higher initial cost, while manual or semi-automatic machines may be more suitable for smaller operations.
2. Consider the Machine's Functionality and Features
Once you have a clear understanding of your needs, the next step is to assess the functionality and features of the food machine. Machines come with a range of capabilities, and it's important to select one that suits your operational needs:
Versatility:
If your production line involves processing various types of food, look for machines that offer flexibility in terms of handling different products. Machines with adjustable settings or interchangeable components can be more versatile and allow for future growth.
Speed and Efficiency:
Machines vary in terms of their processing speed. If you have high-volume production requirements, choose a machine that can handle large quantities efficiently without compromising quality. Machines with high throughput rates are essential in meeting tight deadlines and increasing productivity.
Ease of Use and Maintenance:
A user-friendly machine is critical for ensuring smooth operations and reducing downtime. Look for machines that are intuitive to operate and come with easy-to-understand controls. Additionally, consider the ease of maintenance. Machines that require frequent repairs or complex maintenance procedures can lead to increased operational costs.
3. Assess the Quality of the Machine
The quality of the food machine is crucial for ensuring that your production runs smoothly and consistently. Low-quality machines may result in frequent breakdowns, production delays, and poor-quality products. To assess the quality of the machine:
Build Quality:
Machines should be built with durable, high-quality materials that can withstand constant use in a demanding environment. Look for machines that have a reputation for reliability and longevity.
Compliance with Food Safety Standards:
Ensure the machine meets the relevant food safety and hygiene standards. Food machines should be made from food-grade materials that are easy to clean and sanitize to prevent contamination.
Manufacturer's Reputation:
A reputable manufacturer will produce machines that are built to last and meet industry standards. Research the manufacturer’s history, customer reviews, and industry certifications to assess their reputation for producing high-quality equipment.
4. Consider the Machine's Flexibility and Customization Options
Every food production process is unique, and in some cases, you may need a machine that can be customized to your specific needs. Some machines offer customizable features, such as:
Adjustable settings for different sizes or shapes of food products.
Modular designs that allow you to add or remove components as your needs evolve.
Custom molds or attachments that suit the specific type of food you're processing.
Flexibility in the machine's design can give your business the ability to adapt to new products or changes in consumer demand, which is essential for long-term growth.
5. Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership
While the initial price of the machine is an important factor, it's equally important to evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes:
Operating Costs:
Consider the energy consumption of the machine. Machines that are energy-efficient can significantly reduce long-term operational costs.
Maintenance and Spare Parts:
Factor in the cost of maintaining the machine and purchasing spare parts. Some machines require frequent repairs, while others are designed for minimal maintenance. Ensure you can access affordable spare parts and service support.
Training Costs:
If the machine is complex, you may need to invest in training for your staff. Consider whether the machine comes with training resources or if additional costs will be required for training employees.
6. Ensure Support and Warranty
It's essential to ensure that the manufacturer or supplier offers adequate support for the machine after purchase. This includes:
Warranty:
A comprehensive warranty provides peace of mind in case the machine encounters defects or issues within a certain period. A good warranty will also cover repair or replacement of parts.
Customer Support:
Access to reliable customer service is essential for troubleshooting, repairs, or inquiries about machine operation. Look for manufacturers that offer technical support, maintenance services, and readily available replacement parts.
Installation and After-Sales Support:
Some machines require professional installation, so make sure the supplier provides installation services. After installation, ensure there’s ongoing support to help with any issues that may arise during the machine's operation.
7. Analyze Your Long-Term Goals
When selecting a food machine, think about the future growth and expansion of your business. Machines that meet your current needs may not be sufficient as your business grows. Consider whether the machine can:
Adapt to increased production volume: Can the machine handle higher output as demand for your products increases?
Evolve with new product lines: Will the machine be able to process new types of food products as your product range expands?
What Are the Best Practices for Maintaining Food Machines and Ensuring Longevity?
1. Regular Cleaning and Sanitation
Cleaning is one of the most important aspects of maintaining food machines. Food processing environments can accumulate debris, food residues, oils, and dust, which can interfere with the performance of the machines and lead to contamination.
Daily Cleaning:
Clean the machine's surfaces, components, and any parts that come into direct contact with food. This will help prevent the buildup of residues and bacteria.
Scheduled Deep Cleaning:
In addition to daily cleaning, conduct deeper cleans at regular intervals to ensure that even the hard-to-reach parts of the machine are thoroughly sanitized. This is especially important in food manufacturing, where hygiene standards are critical.
Proper Cleaning Agents:
Use the right cleaning agents and detergents recommended by the machine manufacturer. Harsh chemicals or abrasive materials can damage machine parts and affect food safety.
2. Lubrication and Oiling
Machines with moving parts, such as gears, motors, and conveyors, require proper lubrication to function smoothly. Lack of lubrication can lead to friction, wear, and premature failure of machine components.
Frequent Lubrication:
Regularly lubricate parts that require it, such as joints, bearings, and shafts, to reduce wear and tear and ensure that the machine operates smoothly.
Use Quality Lubricants:
Always use lubricants specified by the manufacturer to avoid any adverse effects on the machine. The wrong type of lubricant can cause parts to deteriorate faster.
Check for Leaks:
Periodically inspect for any leaks of lubricants or oils, as this can reduce the effectiveness of the lubrication and potentially lead to mechanical failures.
3. Inspection and Monitoring
Frequent inspection and monitoring of food machines are essential for early detection of potential issues. Identifying small problems before they escalate can prevent significant breakdowns and production delays.
Routine Inspections:
Set up a regular inspection schedule, checking key parts like belts, motors, sensors, and electrical components. Look for signs of wear, cracks, or misalignments that may require attention.
Monitor Performance:
Use performance data or monitoring systems to track how the machine is operating. Monitoring parameters such as temperature, speed, and pressure can help identify potential issues before they cause malfunctions.
Visual and Auditory Checks:
In addition to performance monitoring, visually inspect the machine for any visible wear or damage. Listen for unusual noises that could indicate that a part is misaligned or malfunctioning.
4. Calibration and Adjustment
Over time, food machines may lose their calibration, affecting the quality of the product and efficiency. Regular calibration and adjustments are essential for maintaining product consistency and operational performance.
Calibrate Sensors and Controls:
Machines equipped with sensors (e.g., temperature, humidity, or weight sensors) should be recalibrated regularly to ensure accurate readings. This is important for maintaining product consistency and quality.
Adjust Settings for Optimal Performance:
Check and adjust machine settings (such as speed, temperature, and pressure) based on the specific requirements of the food being processed. Improper settings can result in inefficiencies or defects in the final product.
5. Proper Storage and Handling
Food machines should be stored and handled properly when not in use. Improper storage or mishandling can lead to rust, corrosion, or mechanical damage.
Store in a Dry and Clean Environment:
When machines are not in use, store them in a dry and clean area to prevent rusting or the accumulation of moisture, which can damage the parts over time.
Avoid Excessive Vibration or Impact:
Avoid placing machines in areas where they are likely to experience excessive vibration or impact, as this can lead to misalignment or damage to sensitive components.
Cover Machines When Not in Use:
Use covers or protective sheets to shield machines from dust, dirt, and moisture, particularly in areas with high humidity or exposure to environmental elements.
6. Timely Repairs and Replacements
Even with regular maintenance, some parts of the machine will inevitably wear out over time. Ignoring minor issues can result in more serious problems and expensive repairs.
Address Small Problems Early:
As soon as you notice any issues, whether it's a slight noise, malfunction, or performance drop, address them promptly. Delaying repairs can lead to more significant damage, requiring costly and time-consuming fixes.
Replace Worn Parts:
Components such as belts, seals, and filters have limited lifespans. Regularly check for signs of wear and replace them before they cause operational failures.
Work with Trained Technicians:
In case of more complex issues, work with qualified technicians who can properly diagnose and repair the machines. Regular servicing by experts will help ensure that the equipment remains in top condition.
7. Training and Proper Operation
Proper operation and training are essential in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of food machines. Well-trained operators are less likely to misuse the machines, which can lead to unnecessary wear and tear.
Train Employees Thoroughly:
Ensure that all employees operating the food machines are thoroughly trained in how to use them properly. This includes understanding the machine’s controls, safety features, and the correct operating procedures.
Encourage Proper Handling:
Operators should be taught to handle machines gently, avoiding excessive force or rough handling that can lead to mechanical damage or misalignment.
8. Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Always refer to the machine manufacturer's guidelines and instructions for maintenance schedules, cleaning, and operational procedures. These recommendations are based on the machine's design and help ensure that it continues to perform at its best.
Adhere to Recommended Maintenance Intervals:
Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance intervals for cleaning, lubrication, inspection, and calibration. These guidelines are designed to optimize the performance and lifespan of the machine.
Use Authorized Parts and Components:
When replacing parts, always use authorized or original equipment manufacturer (OEM) components. Substandard parts may not function correctly and could cause further damage to the machine.
What Are the Latest Trends in Food Machine Technology?
Food machine technology has been evolving rapidly, driven by the increasing demand for efficiency, safety, sustainability, and innovation in food production. As food manufacturers strive to meet global challenges such as supply chain efficiency, labor shortages, and the demand for higher-quality products, technological advancements in food machinery are becoming more sophisticated. Here are some of the latest trends in food machine technology that are reshaping the food industry.
1. Automation and Robotics
Automation has been one of the most significant trends in food machine technology. With the rise of labor shortages and the demand for greater production efficiency, robots and automated systems are playing an increasingly important role in food manufacturing.
Robotic Handling Systems:
Robotic arms are now used to perform tasks such as sorting, packaging, and even palletizing. These machines can operate 24/7 without the need for breaks, significantly improving production speed and reducing human labor costs. They also enhance consistency and minimize the risk of human error.
Automated Ingredient Mixing and Cooking:
Automated systems can handle the precise mixing of ingredients, cooking, and baking, all with minimal human intervention. This reduces the time needed for these processes and ensures consistency in product quality across large production runs.
2. Smart and IoT-Enabled Machines
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into food machinery has led to the development of "smart" machines that are capable of communicating with each other and with operators. These machines are equipped with sensors, data analytics, and cloud technology that enhance their performance and allow for real-time monitoring and optimization.
Real-Time Data Monitoring:
IoT-enabled machines can provide real-time feedback on various parameters such as temperature, speed, and pressure. This allows operators to monitor the machines' performance from a remote location and make adjustments as needed to optimize efficiency and reduce waste.
Predictive Maintenance:
By collecting and analyzing data from machines, IoT technology can predict when a machine is likely to fail or require maintenance. Predictive maintenance helps businesses avoid costly downtime and repairs, increasing the reliability and longevity of the equipment.
3. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Sustainability is a key priority in modern food production, and energy-efficient food machines are a big part of this trend. As businesses look to reduce their carbon footprint and lower operational costs, energy-efficient food machines are becoming increasingly popular.
Energy-Saving Technologies:
Many new food machines are designed with energy-saving features, such as variable-speed drives and optimized motor control, which reduce power consumption without sacrificing performance. These machines help businesses lower their energy costs while contributing to environmental sustainability.
Sustainable Materials and Waste Reduction:
New technologies are also focusing on reducing waste in food production. For example, advanced food processing machines are now designed to extract more value from raw materials, reducing offcuts and improving the yield of finished products. Additionally, sustainable materials are being used to manufacture food machines, reducing the environmental impact.
4. Precision and Customization
The demand for customized food products is growing, and food machines are evolving to meet these needs. Manufacturers are investing in machines that allow for precision control over production processes, enabling the creation of highly customized food products that meet specific consumer preferences.
Precision Cooking and Processing:
Food machines now come with advanced controls that allow manufacturers to precisely manage cooking temperatures, mixing speeds, and ingredient proportions. This level of control ensures that food products meet exact specifications and achieve a consistent taste and texture.
Customization for Different Food Products:
Manufacturers can now use machines that are highly adaptable to different food types. For instance, machines are being developed with interchangeable molds or settings that can handle various food shapes, sizes, and formulations. This customization is particularly important for producers of specialty foods, such as gluten-free or vegan products.
5. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being integrated into food machines to enhance their capabilities. These technologies are enabling machines to learn from historical data, optimize processes, and improve decision-making.
Automated Quality Control:
AI-powered systems are now used in food production lines to identify defects, inconsistencies, or contamination in products. These systems can perform high-speed visual inspections, using computer vision and image recognition to detect problems that might otherwise go unnoticed by human inspectors.
Process Optimization:
AI and machine learning algorithms can analyze production data and identify patterns that help optimize the food manufacturing process. This can lead to better resource management, improved efficiency, and higher product quality.
6. Flexible and Modular Equipment
Flexibility is becoming a priority as businesses need to adapt to changing consumer demands and market trends. Modular and flexible food machines offer scalability, allowing manufacturers to adjust production capacity or reconfigure machines as needed.
Modular Systems:
Modular food machines are designed with interchangeable parts or components, making it easier to upgrade or modify the machine for different types of food production. This flexibility is especially important for businesses that want to expand their product lines or adapt to seasonal fluctuations in demand.
Adaptability to Different Food Types:
Some modern food machines can be easily adapted to handle a wide variety of food types and production processes, making them ideal for manufacturers who want to diversify their product offerings.
7. Enhanced Hygiene and Food Safety Features
With the increasing focus on food safety and hygiene, food machines are incorporating advanced features that reduce the risk of contamination and improve product quality.
Self-Cleaning Systems:
Many modern food machines are equipped with automatic cleaning systems that can thoroughly sanitize the machine without the need for manual intervention. This reduces downtime and ensures that the machines maintain the highest hygiene standards.
Improved Food Handling Systems:
Advanced food handling and processing machines are designed to minimize direct human contact with food, further enhancing food safety. These machines are equipped with features that prevent contamination from environmental factors or improper handling.
8. 3D Printing in Food Production
3D printing technology is slowly making its way into food manufacturing, offering innovative possibilities for creating customized food products. 3D printing in food production allows for precise control over shapes, textures, and ingredients, making it a promising technology for the future.
Custom Food Designs:
3D printers can produce intricate food shapes and designs that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional methods. This is particularly appealing for high-end restaurants, specialty foods, or consumer products that require unique designs.
On-Demand Production:
3D printing also enables on-demand food production, where food can be printed in small batches, reducing food waste and allowing for greater personalization of products.
The latest trends in food machine technology are revolutionizing the food industry by increasing efficiency, improving product quality, and making production more sustainable. From automation and AI to energy-efficient systems and 3D printing, technological advancements are driving the future of food production. As businesses strive to meet consumer demands for quality, customization, and sustainability, staying ahead of these trends will be key to maintaining competitiveness in the market.
If you are looking for advanced food machines that align with these latest trends, visit our website at https://www.gusumachinery.com/ or consider visiting our factory, Food Machine Factory Gusu, for more information on how we can help you enhance your food production processes.


 English
English Español
Español









