Chocolate Chips Machines Enable High-Volume, Consistent Production with Precision Control
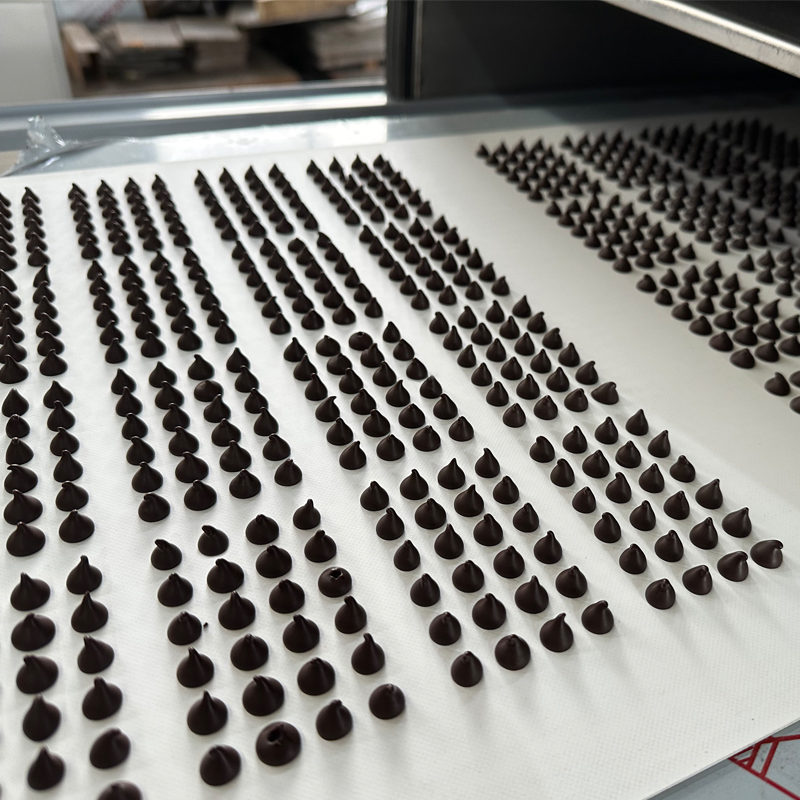
A chocolate chips machine is a specialized piece of confectionery equipment designed to cut, shape, and cool liquid chocolate into uniform chips, drops, or chunks for use in cookies, ice cream, baking mixes, and snacks. Unlike manual chopping or inconsistent extrusion methods, industrial machines deliver exact weight, shape, and tempering—critical for product quality and consumer expectations. Modern automated lines can produce 300–1,200 kg of tempered chocolate chips per hour with ±0.1g weight accuracy, reducing waste and ensuring batch-to-batch consistency. For bakeries, food manufacturers, and private-label producers scaling beyond artisanal output, investing in a dedicated chocolate chips machine is not just efficient—it’s essential for meeting commercial standards.
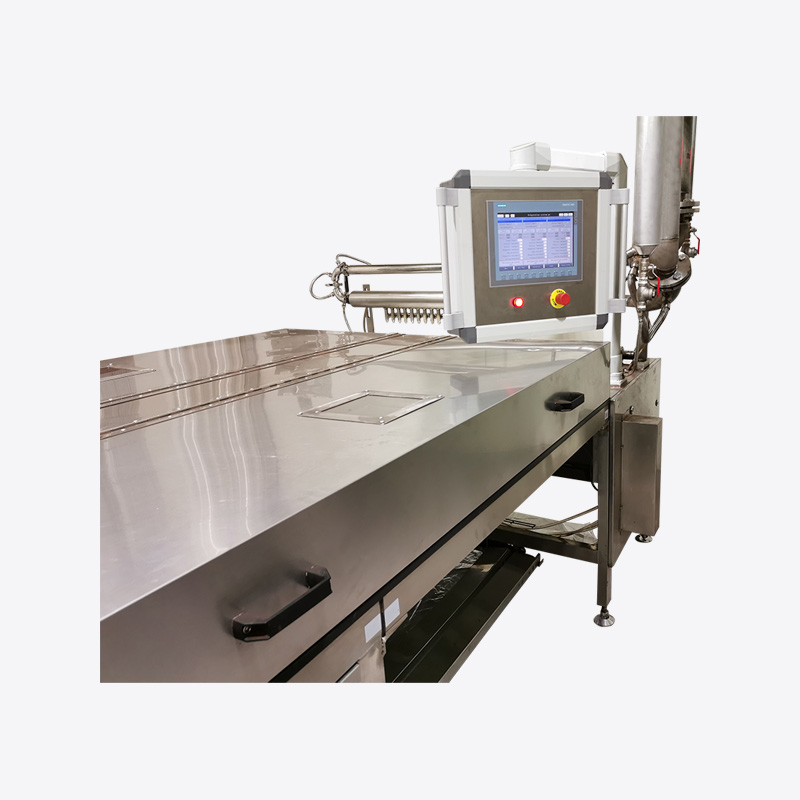
Core Components and Working Principle
Most chocolate chips machines operate on a continuous process involving four key stages:
- Tempering Unit: Heats and cools chocolate to precise temperatures (typically 31–32°C for dark chocolate) to stabilize cocoa butter crystals.
- Depositing System: Uses servo-controlled nozzles to drop measured amounts onto a chilled conveyor belt.
- Cooling Tunnel: Gradually solidifies chips over 8–15 minutes using controlled airflow (10–14°C) to prevent bloom.
- Collection & Sieving: Separates fully formed chips from irregular pieces, which are recycled into the melt tank.
Advanced models integrate real-time vision systems to detect misshapen chips and auto-adjust deposit parameters.
Types of Chocolate Chips Machines by Scale
| Type | Output (kg/hour) | Automation Level | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic Benchtop | 10–50 | Manual deposit, auto cooling | Artisan bakeries, R&D labs |
| Mid-Range Automatic | 100–400 | Fully automatic with PLC control | Regional food brands, contract manufacturers |
| High-Speed Industrial | 500–1,200+ | Integrated with ERP, AI-based QC | Global confectionery giants (e.g., Nestlé, Hershey’s) |
Leading manufacturers include Sollich (Germany), G&G Technologies (USA), and Baker Perkins (UK).
Customization Capabilities: Shape, Size, and Inclusions
Today’s machines go beyond standard teardrop chips. Interchangeable nozzles and molds allow production of:
- Mini chips (3–5mm) for premium ice cream
- Chunky squares or rectangles for bakery bars
- Filled chips with caramel, peanut butter, or fruit gel centers
- Colored or flavored coatings (e.g., white chocolate with matcha)
A 2025 product innovation report noted that 62% of new cookie launches featured non-traditional chip formats—driving demand for flexible machinery.
Tempering Accuracy and Bloom Prevention
The biggest challenge in chocolate chip production is preventing fat bloom—a whitish haze caused by unstable cocoa butter recrystallization. High-end machines use multi-zone tempering with inline viscosity sensors to maintain crystal Form V stability. Cooling tunnels follow strict time-temperature profiles: rapid initial set followed by gradual equilibration. Properly tempered chips from industrial machines exhibit less than 2% bloom incidence after 6 months of storage at 20°C, compared to 15–30% in manually processed batches. This directly impacts shelf life and brand reputation.
Cleaning, Maintenance, and Food Safety Compliance
Chocolate residue hardens quickly, making sanitation critical. Modern machines feature:
- CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems with hot water or food-grade detergent cycles
- Tool-free disassembly of deposit heads and conveyors
- Stainless steel 316L construction compliant with FDA, CE, and EHEDG standards
Scheduled maintenance every 500 operating hours—including lubrication of servo motors and calibration of temperature probes—is recommended to ensure longevity and compliance.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs
While industrial chocolate chips machines require significant upfront investment ($50,000–$500,000+), their operational efficiency offsets costs over time. Key savings include:
- Reduced chocolate waste through precise dosing (losses under 1% vs. 5–8% in manual methods)
- Lower labor costs—1 operator can manage a fully automatic line
- Energy recovery systems in cooling tunnels that cut refrigeration load by 20%
ROI is typically achieved within 14–24 months for businesses producing over 5 tons monthly.

Future Trends: Smart Integration and Sustainable Materials
The next generation of chocolate chips machines integrates IoT sensors for predictive maintenance and blockchain traceability—from cocoa bean to chip. Additionally, manufacturers are adapting machines to handle alternative chocolates: sugar-free, plant-based, or those made with upcycled cocoa pulp. By 2027, 40% of new installations are expected to support “free-from” formulations, driven by health-conscious consumers. As demand for consistent, high-quality inclusions grows across global markets, the chocolate chips machine remains a cornerstone of modern confectionery innovation—transforming liquid chocolate into perfectly engineered bites of indulgence.


 English
English Español
Español









