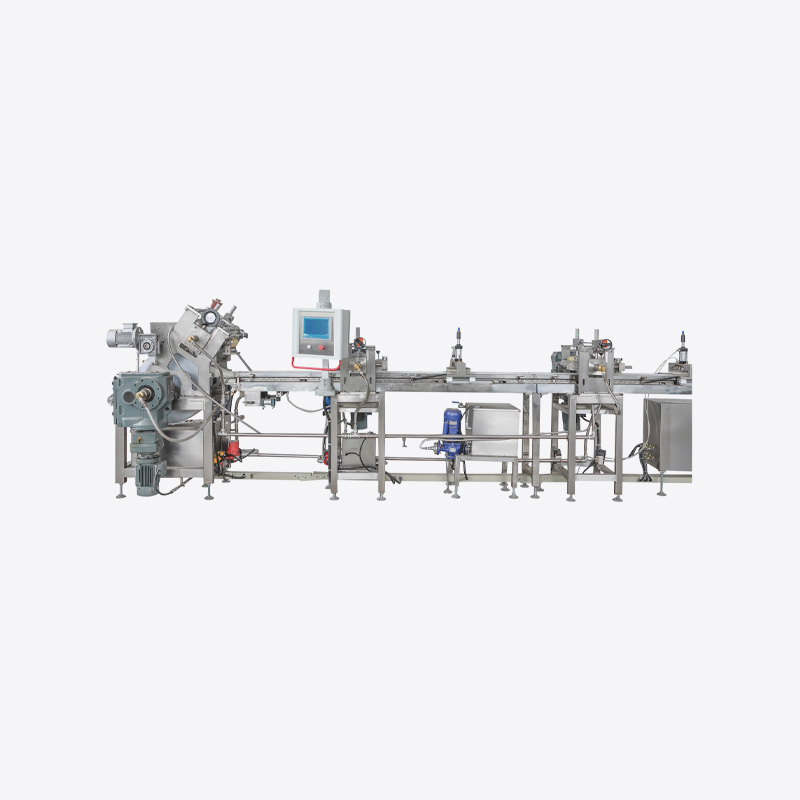
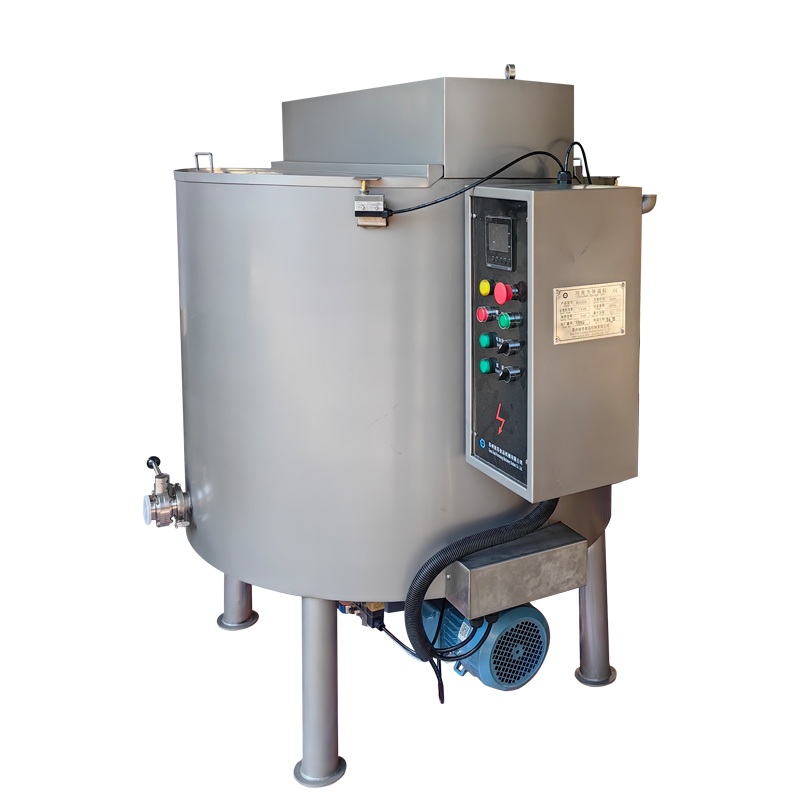
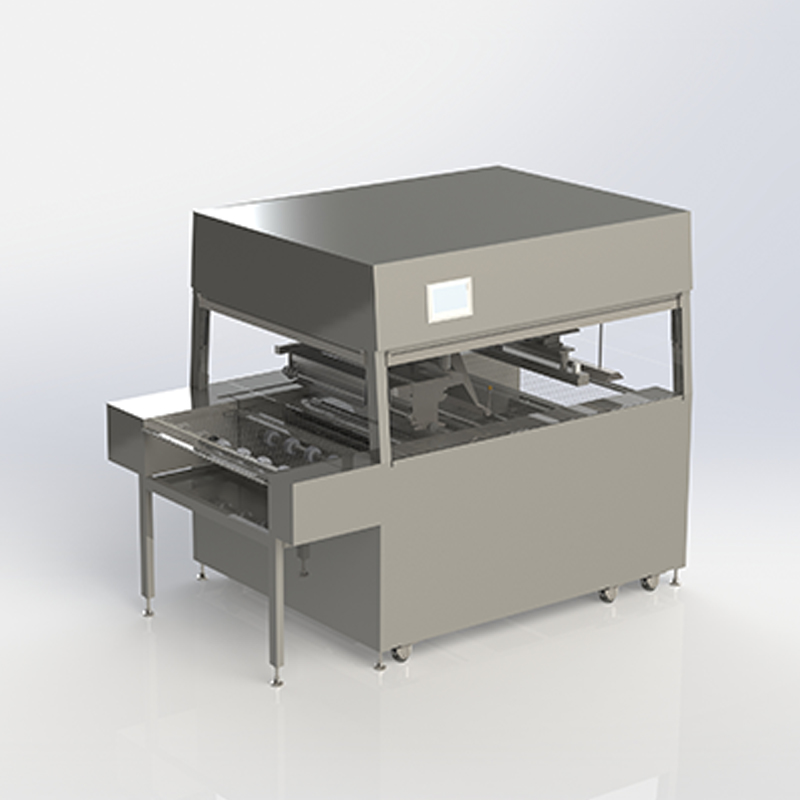
During the chocolate production process, the Chocolate Moulding Line will generate a certain amount of waste. These wastes mainly come from overflow during mold pouring, defective products, residues from demoulding failure, and defective products generated during equipment debugging or line change. If they are not recycled, it will not only cause a waste of raw materials, but also increase the cost of environmental protection treatment and the operating burden of the enterprise.
In order to achieve efficient utilization of resources, improve economic benefits and sustainable development levels, the recycling and reuse of chocolate waste should start from the following aspects:
1. Classification and collection of waste materials
First of all, the waste materials should be effectively classified for subsequent treatment:
Directly reusable waste materials: such as fresh overflow chocolate, which can be directly melted and reused if it is not contaminated.
Waste materials that need to be processed before reuse: Including products with slight defects, such as small cracks, a small amount of bubbles, etc., this type of waste materials need to be crushed, screened and filtered before they can be reused.
Non-reusable waste materials: such as chocolate that is severely contaminated, mixed with foreign matter, or exposed for a long time and deteriorates, must be treated as food waste.
Special waste collection devices are set up in key areas of the production line, such as mold outlets, cooling areas, and demolding areas. Collection tanks and sealed containers made of food-grade materials are used to avoid contamination and maintain stable waste quality.
2. Waste pretreatment
In order to improve recycling efficiency and ensure reuse quality, waste usually needs to undergo the following pretreatment steps:
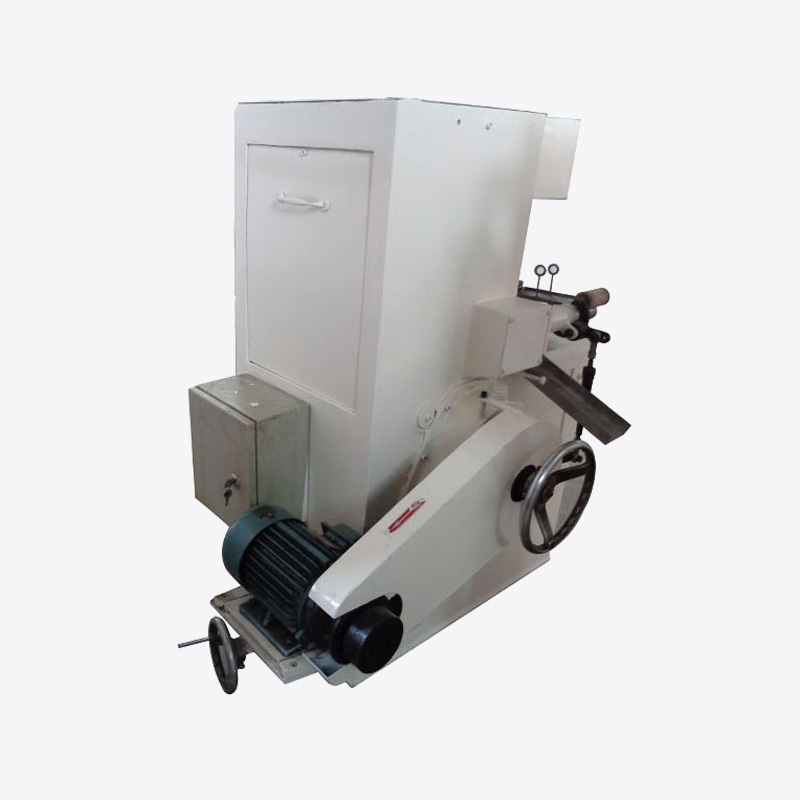
Crushing/shredding: Breaking large pieces of waste into small particles helps to heat evenly and melt quickly.
Screening and magnetic separation: Remove impurities such as paper scraps, plastic fragments, etc., and remove metal particles through magnetic filters to ensure food safety.
Drying treatment (depending on the situation): If the waste contains water or is damp, it should be dried at low temperature to prevent oil emulsification or microbial growth.
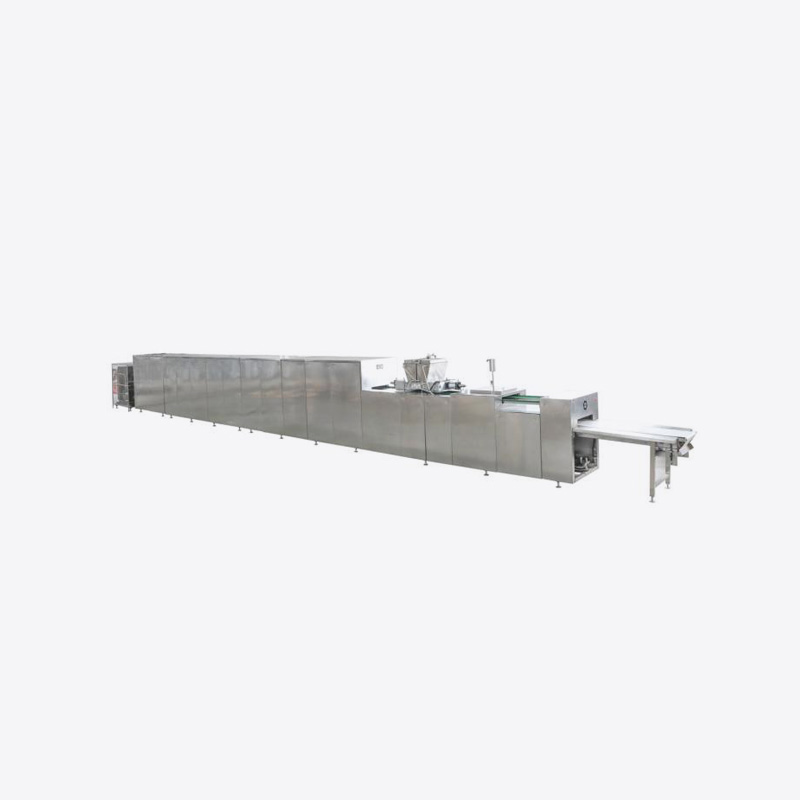

3. Waste remelting and reprocessing
After pretreatment, the waste enters the remelting system, which is the core link of the entire recycling process:
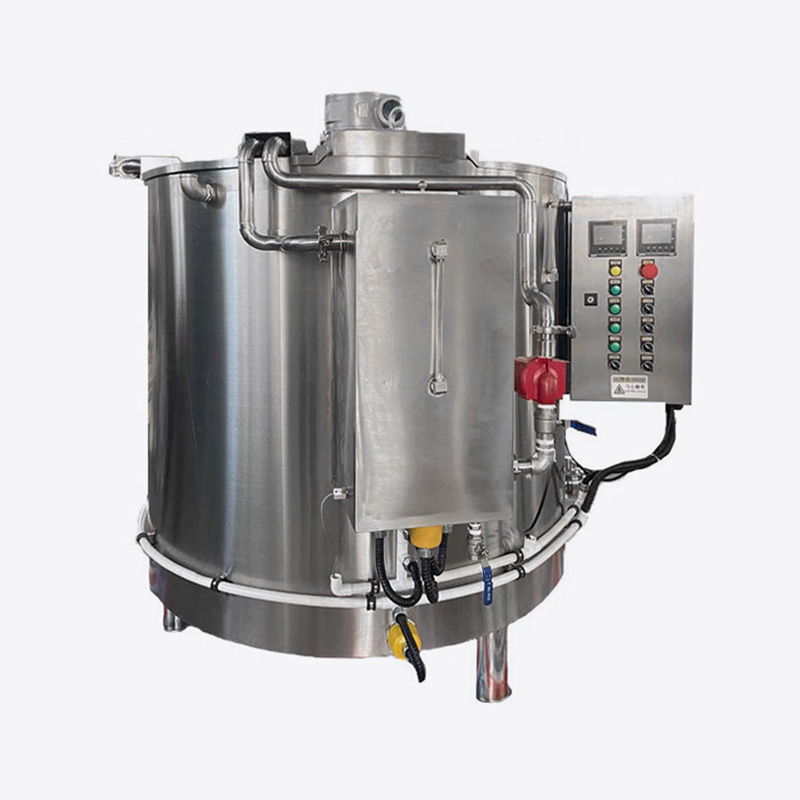
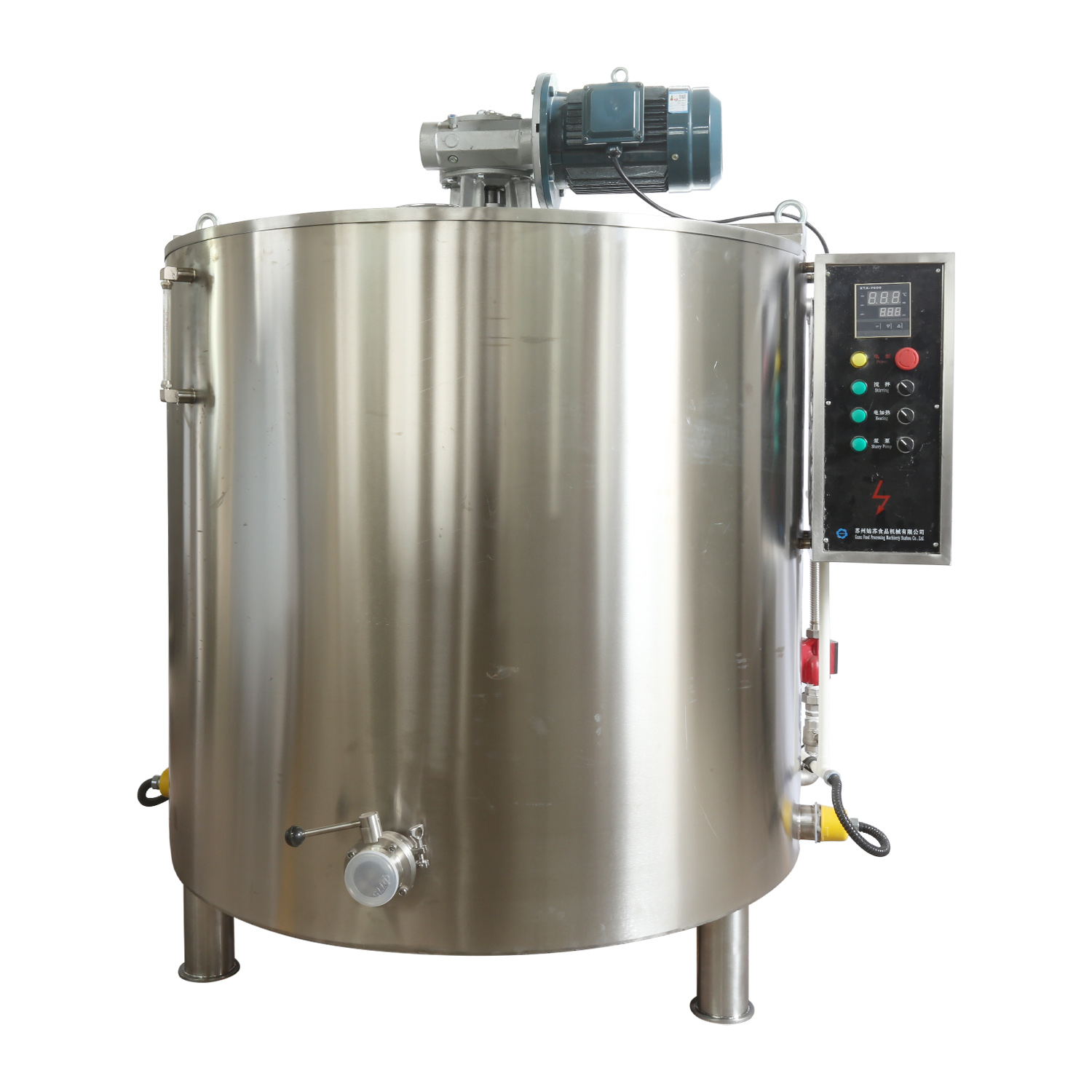
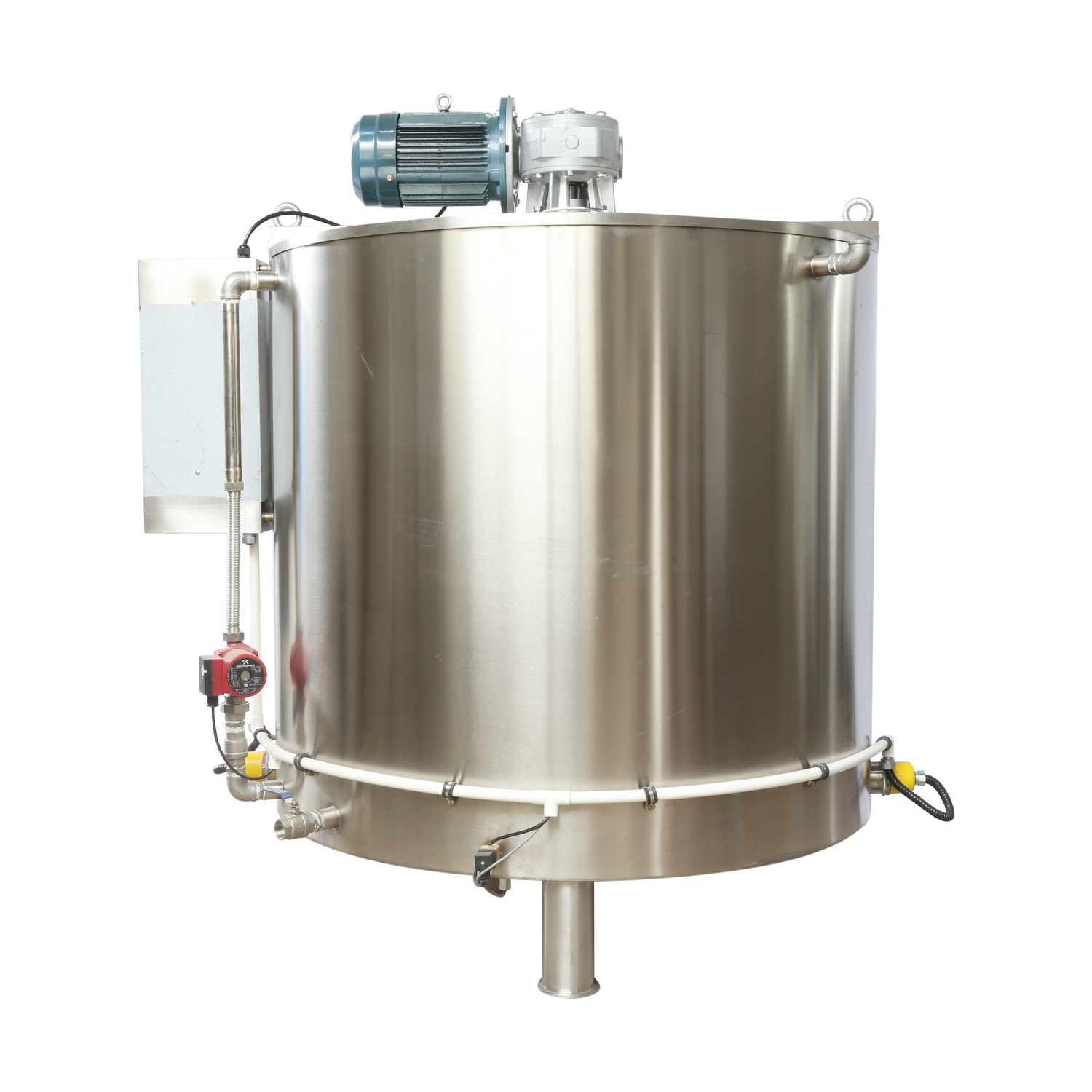
Use a chocolate melting tank or reflux tank with temperature control function to slowly heat the waste to between 40 and 50°C to avoid high temperature causing scorching or composition changes.
Equipped with a stirring device to keep the chocolate temperature uniform and prevent local overheating or precipitation.
Install a multi-stage filtration system, such as a stainless steel filter or a self-cleaning filter, to remove impurities and ensure the purity of the recycled chocolate.
The melted chocolate can be mixed with new materials in a certain proportion and then put back into the production line. It is generally recommended that the proportion of waste material reuse be controlled between 10% and 20% to ensure that the taste, texture and appearance of the finished product are not affected.
IV. Mixing ratio control and quality monitoring
To ensure stable product quality, the use of waste materials must be strictly controlled:
Set up an automatic weighing and ratio control system during the batching stage to accurately control the ratio of new and old chocolate.
Regularly test the color, odor, viscosity, microbial indicators, etc. of the recycled chocolate to ensure that it meets food safety standards.
If it is found that the reuse of waste materials causes problems such as rough texture, oil oxidation, and flavor changes in the product, the reuse ratio should be adjusted in time or some fresh materials should be replaced.
5. Automation and intelligent management (advanced solution)
With the development of intelligent manufacturing, more and more companies are beginning to introduce automated recycling systems:
Establish an integrated recycling system to integrate multiple links such as waste collection, crushing, melting, filtering and transportation, reduce manual intervention and improve efficiency.
Use the MES system to record the quantity, reuse ratio and quality inspection results of each waste recovery to achieve data management and continuous optimization.
Explore the application of AI prediction models, analyze the impact of different waste ratios on the quality of finished products through machine learning, and assist in formula adjustment and process optimization.
6. Environmental protection and sustainable development strategy
Environmental protection and energy saving should also be emphasized during the recycling process:
The recycling system uses green technologies such as energy-saving motors and waste heat recovery devices to reduce energy consumption.
Statistics on the chocolate recycling rate are used as one of the environmental performance indicators in the company's ESG report.
For waste containing packaging materials, mechanical or manual separation should be carried out first, and they should be treated separately to avoid cross contamination.
Although the waste generated by the chocolate molding line is inevitable, it can be fully reused to the maximum extent through scientific classification, efficient pretreatment, precise remelting and mixing control. This will not only significantly reduce raw material waste and production costs, but also enhance the company's environmental image and market competitiveness.


 English
English Español
Español









