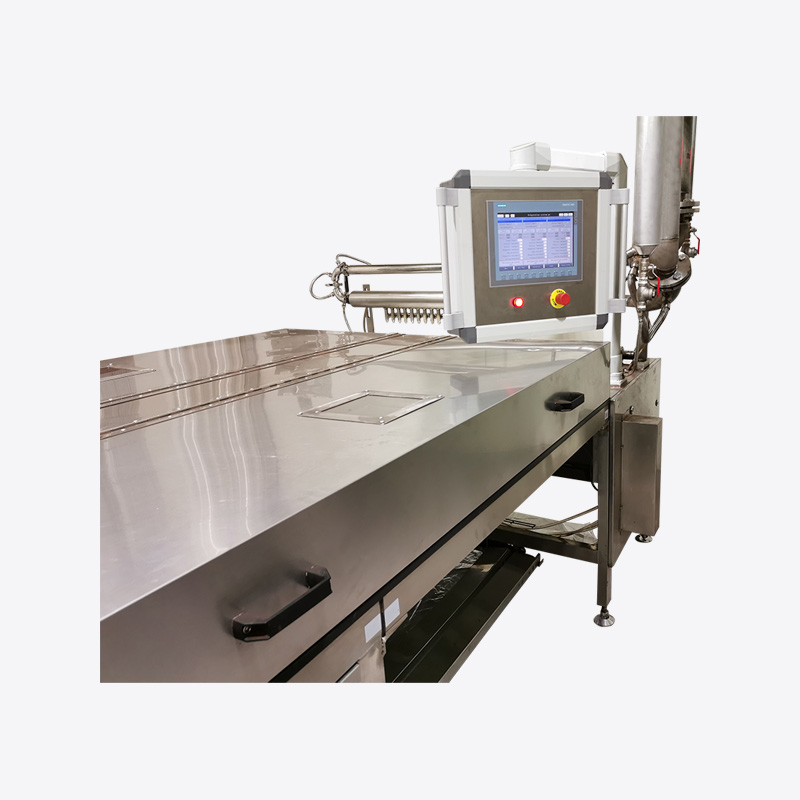
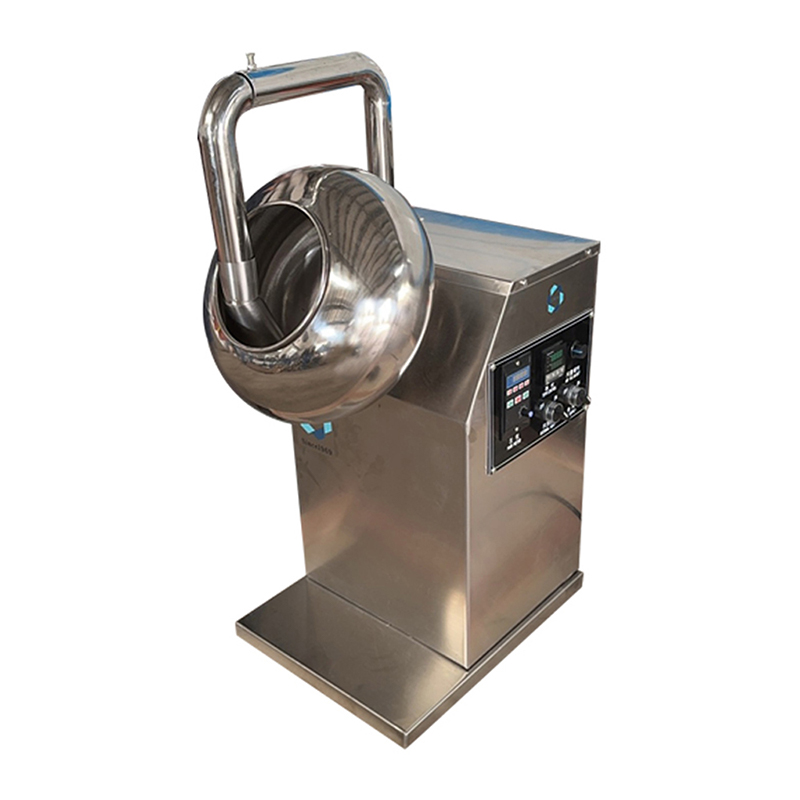
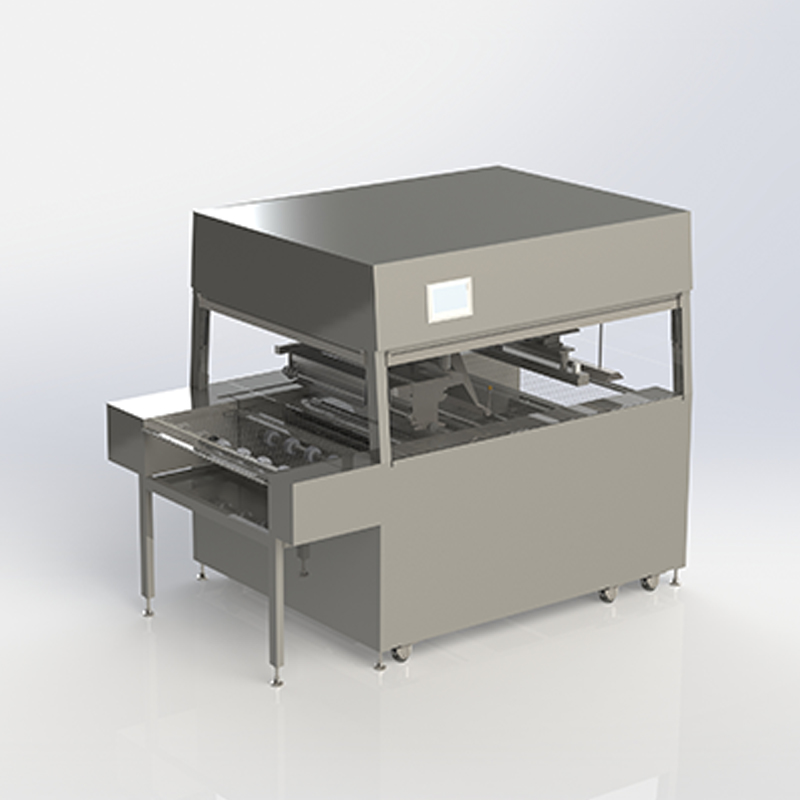
In the food industry, Chocolate Coating Pans are widely used to coat the surface of candies, nuts, biscuits, rice cakes and other foods with a smooth, beautiful and rich chocolate layer. However, in actual operation, the chocolate coating often has problems such as uneven thickness, poor adhesion and poor glossiness, which affect the quality and market competitiveness of the product. Among them, temperature control and stirring speed adjustment are two key factors to ensure the uniformity of the chocolate coating.
Temperature is the core parameter that determines the fluidity and viscosity of chocolate. Chocolate is a material that is extremely sensitive to temperature, and its physical properties will change significantly with changes in temperature. Taking common tempering chocolate as an example, the ideal working temperature of dark chocolate is usually between 31–32°C, milk chocolate is 30–31°C, and white chocolate is slightly lower, about 29–30°C. If the temperature is too high, the cocoa butter in the chocolate may precipitate, resulting in oil spots or loss of gloss on the surface; if the temperature is too low, the chocolate will become too viscous, the fluidity will decrease, and it will be difficult to evenly coat the surface of the food.
When using a Chocolate Coating Pan, it should be equipped with a high-precision temperature control system and set the appropriate working temperature according to the type of chocolate used. At the same time, the temperature changes should be continuously monitored during the coating process to avoid unstable chocolate performance due to environmental fluctuations (such as room temperature changes or heat changes caused by continuous feeding). In addition, it is also possible to consider adding an appropriate amount of emulsifier (such as lecithin) or oil components to the chocolate to improve its fluidity and wettability, thereby enhancing its ability to evenly cover the surface of the food.
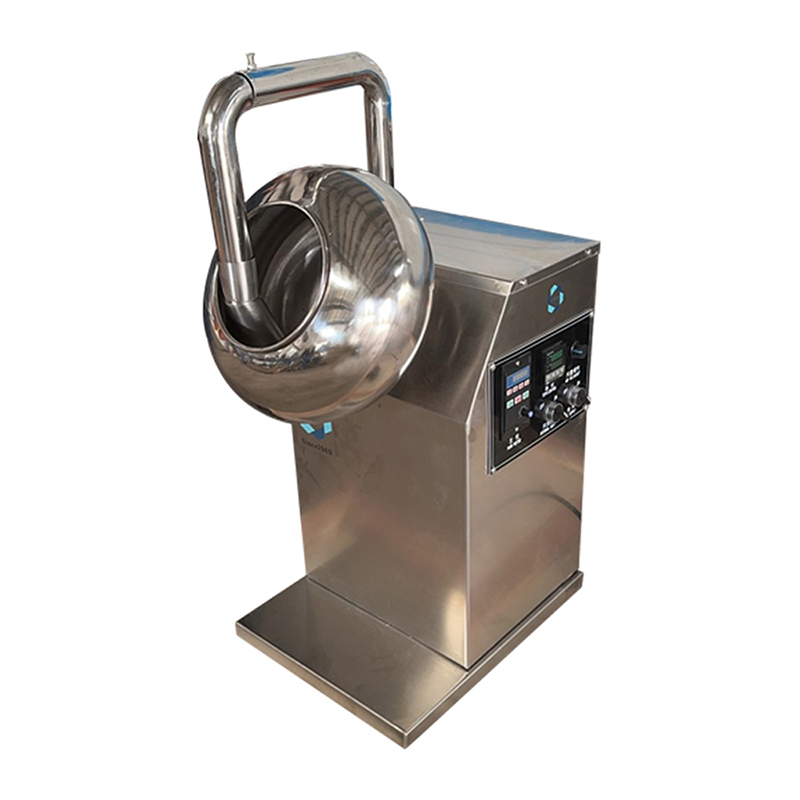

The stirring speed directly affects the degree of mixing uniformity between chocolate and food. During the chocolate coating process, the stirring device drives the food material to roll continuously, so that it is fully in contact with the molten chocolate and forms a uniform coating. If the stirring speed is too fast, it is not only easy to cause chocolate splashing, but also may bring in air and produce bubbles, affecting the density and appearance quality of the coating; while the stirring speed is too slow, it cannot effectively promote the uniform distribution of the food material, resulting in chocolate accumulation in some areas and incomplete coverage in some areas.
Generally speaking, the stirring speed should be adjusted according to the volume, density and shape of the food. For example, for lighter foods (such as marshmallows, rice cakes, etc.), it is recommended to use a lower stirring speed to prevent the material from being crushed or ejected from the pot; while for larger and denser foods (such as nuts, cookies, etc.), the stirring speed can be appropriately increased to enhance the contact efficiency between chocolate and food. In addition, it is recommended to conduct small batch tests before formal production, and gradually optimize the combination of stirring speed and time to find the best operating parameters.
In addition to temperature and stirring speed, factors such as the texture, viscosity, whether the chocolate itself has been well tempered, and coating time will also affect the final coating effect. Therefore, in practical applications, these variables should be considered comprehensively, and the best process matching should be achieved through multiple tests and adjustments.
By accurately controlling the working temperature of the Chocolate Coating Pan and reasonably adjusting the stirring speed, the uniformity, adhesion and overall quality of the chocolate coating can be significantly improved. This not only helps to improve the appearance and taste of the product, but also improves production efficiency and yield rate, bringing higher economic benefits and market competitiveness to the company.


 English
English Español
Español









